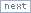
함수 오버로딩 (이미 생성자에는 2개의 변수가 0으로 초기화 된 상태)
문자열의 길이를 구한 다음, 메모리를 동적할당 받아 확보한 후,
해당 문자열을 널까지 포함하여 cpString에 복사한다.
복사 함수, 내용은 위에 함수와 흡사. 레퍼런스 변수를 인자로 받는다.
소멸자. 동적 메모리를 제거한다.
cout << ???형태를 함수로 만들기 위한 과정이다.
cout은 ostream형이고 포인터가 인자가 된다.
<<에 해당하는 함수이다. 첫 번째 인자의 ,cout의 주소를 받고, 출력할 대상이 되는 2번째 인자로 가진다.
위에 있는 print()함수를 호출하기만 하면 cout <<??형태가 가능해진다.
반환형이 ostream&라는 것에 유의하자.
대입 연산자 함수
+연산자 함수
'c++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 11월 25일 연산자 오버로딩 (정리 중) (0) | 2013.11.25 |
|---|---|
| 11월 21일 추상클래스 (0) | 2013.11.21 |
| 11월 13일 상속 클래스의 생성과 소멸 (0) | 2013.11.13 |
| 11월 13일 상속 클래스 기초1. (0) | 2013.11.13 |
| 11월 12일 파일 임의 접근 (0) | 2013.11.13 |